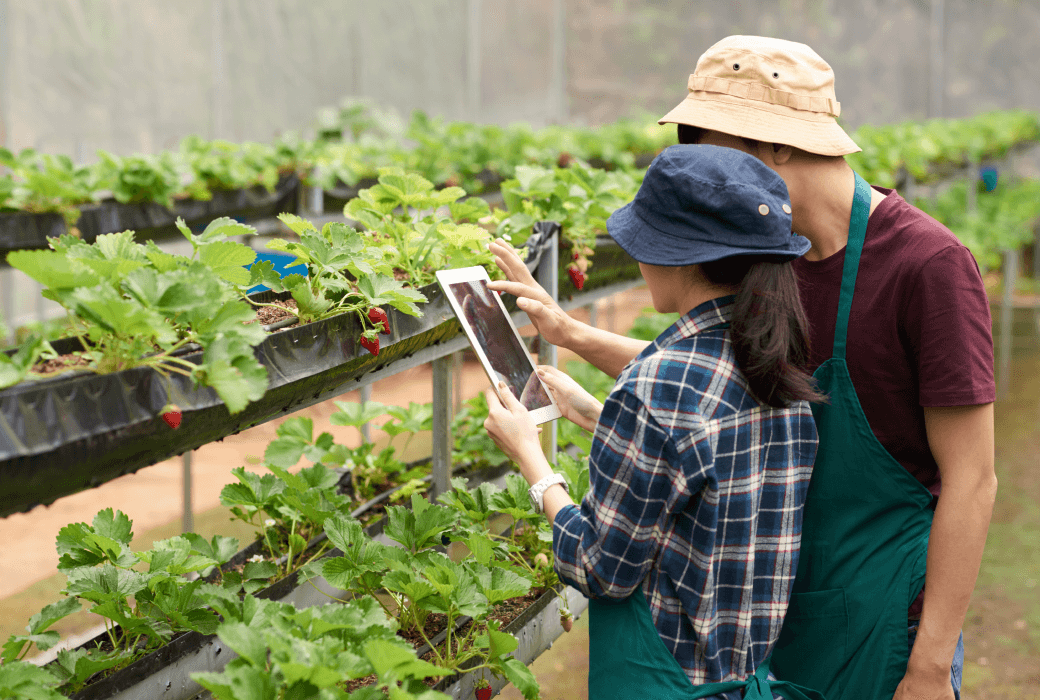
How do farmers keep up with the rising demand for food, man-hours, and uncertain weather in order to stay efficient and minimize costs?
The traditional approach to farming wastes resources and deals with minimal consistency in yields from year to year, making it unreal to measure against the challenges agriculture faces today.
Farm automation is the answer. Robotics, sensors, and generative artificial intelligence deployed in farming help optimize operations, resource management, and productivity, touching the largest issues confronting agriculture today. According to Statista, the world market for smart agriculture is expected to reach nearly $33 billion by 2027. That highlights a growing trend and dependence on farming technology among farmers.
This blog will guide you on precisely what farm automation means, its benefits, and what the future of farming is by using smart and automated systems.
What is Farm Automation?
Farm automation refers to the employing of mechanics and electronics in activities such as planting, watering, fertilizing, harvesting, and growing crops, which were manually done. It cuts the labor force, increases accuracy, and enhances effectiveness, which results in better management of crops and increased productivity.
For instance, an automated irrigation system monitors soil moisture and other weather conditions through sensors so crops are watered in the right amount. Besides saving water, it ensures healthier crops and less waste.
Key Benefits of Farm Automation
Farm automation tackles challenges like feeding a growing population, labor shortages, and the need for efficient food production. Its benefits are revolutionizing agriculture.
Increases Productivity:
The automated systems ensure high productivity. Multiple planting, harvesting, and monitoring will be completed faster. This enables the farmers to grow more crops in shorter periods.
Lowers the Need For Labor:
Labor shortages are less likely to be experienced in farming activities due to automation. Plenty of processes and operations that need many laborers can be executed using machines. This ensures that the operations are effective even when there are few hands.
Improves Accuracy:
Sensor systems, UAVs, and other technologies deliver accurate information. They also ensure that water, fertilizers, and pesticides are applied accurately. This maintains the health of the crops at lower levels of wastage.
Improves sustainability:
Automation enhances the sustainability of the farm. Optimizing resources such as water and fertilizers reduces environmental footprint. This makes the farming practice more sustainable.
Farming using data technology:
Automation in agriculture allows farmers to possess data in real-time. This assists them in making the right choices about activities on the farm. This results in effective management of the farms and the economic quality of the produce.
Smart Farming: The Next Level of Agriculture
“Smart agriculture,” most often referred to as precision farming, is an advancement in farm automation by many degrees and employs AI, IoT, machine learning, etc. The farms that embrace this technology have a network of different information-gathering equipment such as sensors, drones, and automated machinery in order to make timely decisions on the efficiency of all agricultural activities undertaken.
Farm automation is undoubtedly a core component of smart farming because it is the backbone needed to implement these high-tech techniques.
Real-World Examples of Farm Automation
To enhance their functionality, several farms across the globe are on the verge of adopting automation techniques. Many are designed to include:
Robotic Harvesters:
Robotic harvesters can now easily program robots to carry out crop harvests, such as fruits and vegetables, where only the ripe produce is picked, minimizing the gathering duration of crops.
AI-Powered Monitoring Systems:
Such drones deploy an AI system for crop health, moisture content in the soil, and also the presence of harmful insects. This allows the farmer to avoid any losses by correcting the situation in advance.
Blockchain for Traceability:
A number of farms are taking advantage of the blockchain solution in order to know the path of their products from the farm gate to the last consumer. This improves traceability, supply chain management, and the trust of the consumers.
How Much Do Farming Robots Cost?
The price range of farming robots varies according to their function and capabilities. Basic robotic systems could cost around $50,000, on average, while expensive systems such as autonomous tractors or robotic harvesters could go from $100,000 to $500,000. Although this might look quite pricey, such a degree of assets is often compensated for with lower expenditure in terms of labor in the long run, as well as the enhancement of productivity.
To What Extent Is Farming Automated?
The adoption of automated systems in agriculture is on the rise; however, this degree varies appropriately according to region and type of agriculture. Worldwide, only about 5-10% of farming operations are automated. In developed economies, the situation is better as more than 30-40% of large-scale farming, especially for crops such as wheat, corn, or soybean, is mechanized.
While there is some growth in the use of automation in agriculture in developing regions, the uptake rate is still very low, as so far, under 5% of farming is automated. The major reasons are the high expenses and lack of technology. High-value and greenhouse farming uses more precision agriculture, with techniques involving drones, sensors, AI, and robotics. New technology will advance automation possibilities in agriculture.
Challenges of Implementing Farm Automation
Various challenges arise when attempting to automate farming:
High Costs:
Fully mechanizing entails using modern mechanized equipment, robotics, and advanced technologies, all of which are costly, making it difficult for small-scale farmers.
Technical Complexity:
Automation systems are complex in nature and need special skills and knowledge for installation, usage, and even maintenance, which are usually not readily available in many rural farm settings.
Infrastructure Limitations:
A number of areas, particularly developing countries, have insufficient facilities such as power and high-speed internet, which are essential for the installation of automated systems.
Labor Displacement:
The introduction of automation technologies can cause the loss of jobs, especially in agricultural sectors, which leads to issues about employment and even worries about the social aspects of rural societies.
Customization for Different Crops:
Farm automation is usually used to suit only certain crops and specific farming methods; thus, its use for various agricultural requirements is limited.
Data Privacy and Security:
With the growth of IoT connectivity and data-driven analytics as the backbone of automated farms, concerns arise about the danger of breaches and hacking, among other data insecurities.
Regulatory Barriers:
In certain places, policies and legal issues encourage a slow uptake of crewless automobiles, drones, or genetically engineered plants.
Future Trends of Farm Automation
Several important trends will be responsible for revolutionizing agriculture in terms of farm automation:
Integration of AI and Machine Learning:
AI will be able to improve crucial decision-making in precision farming, smart planting and harvesting, and smart irrigation through predictive analysis and real-time processing of data.
Vertical and Indoor farming Automation:
There will be much more automation in vertical and indoor growing systems dedicated to maximizing the utilization of available space and other resources to increase crop production. Systems powered by AI will manage lighting, temperature, and water, amongst many other aspects of the farm; such farms will be extremely resourceful.
Sustainable Automation:
There will be more regard for thermal and environmentally friendly automation, such as machinery driven by solar energy equipment, automation in organic farming, and precision agriculture practices aimed at minimal control of water and pesticides.
Utilization of Blockchain Technology:
Implement blockchain within the automated systems that trace provenance, making food supply chains transparent and instilling trust into the network.
Cobots:
More flexible and compact robots will be brought into the market to handle agricultural workloads such as harvesting sensitive crops or packaging vegetables. These are not intended to replace labor in total.
Wrapping Up
Farm automation is revolutionizing agriculture, and it makes farming smarter, more efficient, and more friendly for the environment. The easier way to produce more with fewer resources and even lower labor costs is through the use of smart technologies and automated systems. Such implementations result in yield improvements for crops, less or even no waste, and optimized water and fertilizer.
High up-front costs and the requirement of technical skills are great challenges, but the long-run benefits are definitely worth exceeding those hurdles. It is not hard to predict that the future of farming is going to be greater automation in the industry, with innovations in robotics, AI, and data analytics.
With technology improving day after day, we can expect more farms to adopt such solutions to achieve far better farming results, increased food security, and a sustainable future for agriculture across the globe.
With VisionX, you can revolutionize your farm automation by leveraging advanced computer vision and machine learning to monitor crop health, optimize resource use, and enable autonomous operations, ensuring increased efficiency and higher yields for your agricultural business.